Page History
| Table of Contents |
|---|
eagle-i SVN
The latest set of eagle-i ontology files can be obtained from the open.med Harvard SVN repository. The checkout will provide all the needed files to work with the eagle-i ontology.
...
If any of the files in this directory are opened in Protege without first running the scripts to generate a local ontology, or a correct “catalog-v001.xml” file is already in the repository, the OWL imports listed in the application files will be resolved online and will not show the “trunk” (i.e. local files) eagle-i ontology, i.e. the latest files generated from the ISF trunk. This is because in our current setup, there are no "trunk ontology files" per se; there are only "trunk modules" that need to be “built” to get the generated trunk eagle-i ontology. Without doing this, what you see in Protege is a combination of the “trunk eagle-i application ontology” files and the “latest release eagle-i ontology” (as long as the PURLs are kept up to date with the latest ontology release). This is probably not what you want. The right thing to do is to first generate the local ontology to get the current (i.e. trunk) ontology files and the catalogs, and then open the files as needed. Alternatively, if you are only interested in the latest development version of the eagle-i ontology without having to build locally from the source modules, you can obtain pre-built development files from: https://www.eagle-i.net/ero/.
src/eagle-i/public
...
When the ontology files are generated locally (see build section), the ontology files are generated in this directory, along with the required imports and appropriate Protege catalog files. The combination of the application files from SVN and the files from the local ontology generation should match the same set of files that are generated during a Bamboo build. The scripted local ontology generation has been tested on Windows and Linux and appears to be working without problems.
src/isf/module
This contains directories and files needed to generate the eagle-i ontology files. The individual module sub-directories contain the module configuration files that are used by the tooling to generate the corresponding eagle-i ontology files during a local ontology generation. See the tooling documentation for further details.
src/isf/module-scripts
This directory contains Windows and Linux scripts that can be used to generate:
...
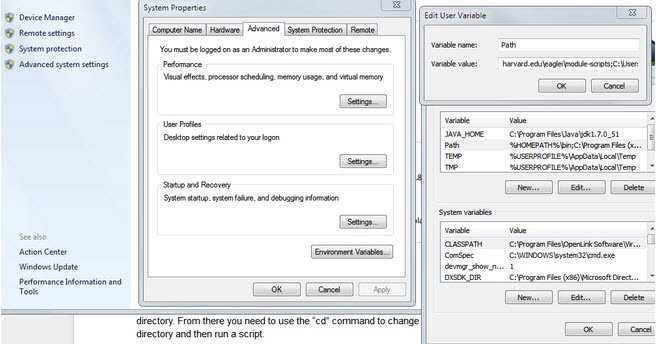
If you are not in the module-scripts directory but would like to run a script without first changing to that directory, you have two options. Either type the full/relative path to the script file in the shell (for example, you might need to type “src/isf/module-scripts/ei-...”) or add the “module-scripts” directory to the Windows Path environment variable. Google for how to set Windows environment variables and you can adjust your “user” Path variable to include this directory. See the following image as an example. Google for instructions for doing this.
src/isf/ontology
This is an SVN external to the “VIVO-ISF Ontology” from GitHub (but the ontology directory only, not the root directory of the GitHub repository): https://github.com/vivo-isf/vivo-isf-ontology/trunk/src/ontology
by using the GitHub SVN integration described here: https://help.github.com/articles/support-for-subversion-clients/
This pulls in the “VIVO-ISF ontology” files that are needed to build the eagle-i ontology files. An SVN update done from the root of the eagle-i trunk checkout should pull in any ISF changes unless the external is pinned to a specific ISF commit. Currently the external is following the latest ISF commits.
src/isf/tools
This is an SVN external that follows the “eagle-i” Git branch from the following location: https://github.com/vivo-isf/tools/tree/eaglei/tools/owlcl
This brings in an eagle-i specific revision of the VIVO-ISF tools to use for the eagle-i ontology build. No need to change anything here until there is some issue with the build tools. The eagle-i branch of the tools is currently the same revision as the master branch. However, having a dedicated branch for eagle-i allows for some flexibility if there is a need to diverge from the master revision when needed.
eagle-i ontology files
The eagle-i ontology is composed of a set of static application specific OWL files that are maintained manually, and a set of dynamically generated OWL files that are generated from the ISF ontology based on module configurations.