This page discusses SHRINE's networking requirements for SHRINE versions 4.2.0. The discussion assumes an intermediate level of TCP/IP networking knowledge.
SUMMARY
The following subsections summarize the networking requirements, which are organized by roles. Please follow only the subsection that applies to your site.
For a downstream site connecting to a SHRINE hub:
- The downstream site must allow TCP traffic initiating from its tomcat process to reach the SHRINE hub, with the destination TCP port set to 6443. From the perspective of the downstream site, this traffic will be going outbound and maintained statefully. The downstream site does not need to explicitly allow any reciprocal traffic from the hub back to the site, because the site and the hub will exchange all SHRINE-related application data using the single stateful TCP session that the downstream site initiates. Most institutions allow unrestricted outbound Internet access; this policy should be sufficient.
- The downstream site must configure its firewalls and routers to allow users at the site to access its own SHRINE server, on the TCP port of its choice (the default is TCP port 6443). Because of the wide variety of internal network configurations it is not possible for us to anticipate all feasible permutations. If in doubt, the remote site is strongly advised to check with its networking team for further details and before finalizing any networking decisions.
- If the network is using external message-oriented-middleware (AWS SQS or Kafka) the downstream site must allow TCP access initiating from tomcat to that system.
For a SHRINE hub accepting connections from downstream sites:
- The hub must allow TCP traffic from remote sites to reach its own SHRINE port (the default is TCP port 6443). From the perspective of the hub, traffic coming from downstream sites is considered inbound. Each site will initiate its own TCP connection to the hub, and - once the connection has been established - the hub and the site will use that single TCP connection to exchange all SHRINE-related application data. Both the hub and the remote site will maintain that single connection for as along as SHRINE is running on both ends. The hub does not use any other TCP connection to communicate with the site. The hub administrator needs to exercise caution when configuring network access control, so that the integrity and security of the hub can be maintained.
- If the hub administrators intend for users to access the hub directly then they must grant user access to the hub's SHRINE application (the default is TCP port 6443).
- If the network is using external message-oriented-middleware system (AWS SQS or Kafka) the hub site must allow TCP access initiating from the hub's tomcat to that system.
- If the hub is hosting an external message-oriented-middleware system (Kafka) the hub must allow TCP access initiating from the hub's or any downstream node's tomcat to that system.
DISCUSSION
Network Architecture for SHRINE
Starting with SHRINE 2.0.0, the topology of a SHRINE network was greatly simplified. All that each remote site needs to do is to allow its SHRINE host to have access to TCP port 6443 of the hub. Modern firewalls are typically "stateful" by design. A stateful firewall is aware of the beginning, middle, and end of each connection (particularly TCP connections), and it will maintain each connection for as long as the endpoint application requires it. SHRINE takes advantage of a single, stateful TCP connection that the remote site initiates to allow the site and the hub to exchange all SHRINE-specific data. The downstream site is no longer required to configure an "inbound" (from its perspective) firewall rule to accommodate any "reciprocal" network traffic from the hub. Typically, many organizations allow unrestricted outbound Internet access for their hosts, and in such situations this policy is sufficient for the remote site.
This simplification of networking requirements has two advantages:
- It greatly reduces the number of network connections required in any SHRINE network, and
- In the event of a network-layer problem, troubleshooting is made easier since there are fewer components and pathways involved.
Troubleshooting Connectivity Issues in a SHRINE Network
When troubleshooting connectivity issues, the site administrators must work with the hub administrators to determine the status of network connectivity between the site and the hub. One popular tool is tcptraceroute. The tool utilizes the basic principles of the traditional traceroute program adapted to work with TCP packets. It sends out TCP packets that have the "SYN" flag enabled for increasing values of time-to-live (TTL) until one such packet reaches the destination, or TTL reaches its default limit of 30, whichever comes first. Using tcptraceroute can determine the state of network connectivity between the remote site and the hub.
The following diagram illustrates a fictitious SHRINE network of one hub and one remote site. In this scenario, the SHRINE server has been configured to accept inbound connections to the default TCP port of 6443. Also, the hub and remote sites each have additional networking equipment that may affect routing and/or firewall policies, as shown in their respective blue boxes.
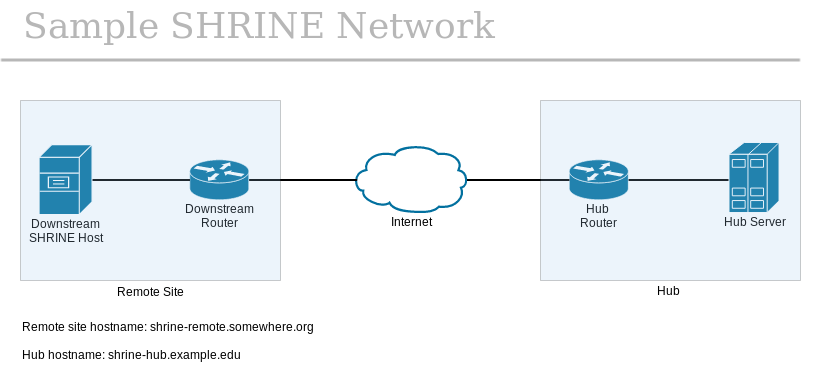
To use tcptraceroute to confirm network connectivity, the remote site administrator will run the utility from her own SHRINE host and point it at the hub. For each hop along the network path, tcptraceroute will send a TCP packet with SYN flag enabled and with the destination port of TCP 6443, until the final TCP packet is sent to the SHRINE server itself or the TTL exceeds the default value of 30. If the SHRINE server is available to the remote site's connection attempt within the hop and time limits of tcptraceroute, then the remote site will see an output like below:
traceroute to shrine-hub.example.edu (xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx), 30 hops max, 60 byte packets 1 * * * 2 * * * 3 * * * 4 * * * 5 * * * 6 * * * 7 * * * 8 * * * 9 * * * 10 * * * 11 * * * 12 shrine-hub.example.edu (xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx) <syn,ack> 95.025 ms * *
In this output, because TCP port 6443 is not commonly used by applications as a listening port it is no surprise that hops 1 through 11 do not respond to the TCP packet within the allotted time. But because the hub is configured to respond to any TCP handshake on port 6443, the last line of the output confirms that the hub replies with a TCP packet that has both SYN and ACK flags enabled. Note that the tcptraceroute utility does not actually complete the entire three-way TCP handshake, so no actual connection is created with the hub.
The remote site is responsible for ensuring that all equipment under its control are configured to facilitate end-to-end communication for SHRINE. Importantly, the remote site is strongly discouraged from interfering with this communication through the use of in-line application proxies because a misconfigured proxy can exert deleterious effects on application payload in TCP packets.