Page History
...
Referenced taxonomies can live in the ero.owl core, or in the extended ontologies. For example, the 'technique' referenced taxonomy lives in ero.owl and is used to record methods related to a given resource, while the 'material anatomical entity' referenced taxonomy that lives in the uberon.owl extended ontology file is used to record the origin of things like 'cell lines' or 'biological specimens'. "Core Reference Taxonomies" are those that live in the core ero.owl file (e.g. 'technique', 'organization', 'data format specification', 'measurement scale'). "Extended Reference Taxonomies" are those that live in an extended ontology file (Uberon, GO, MP, Pato, DOID), e.g. 'life cycle stage', 'material anatomical entity', 'disease'.
Ontology
...
Structure
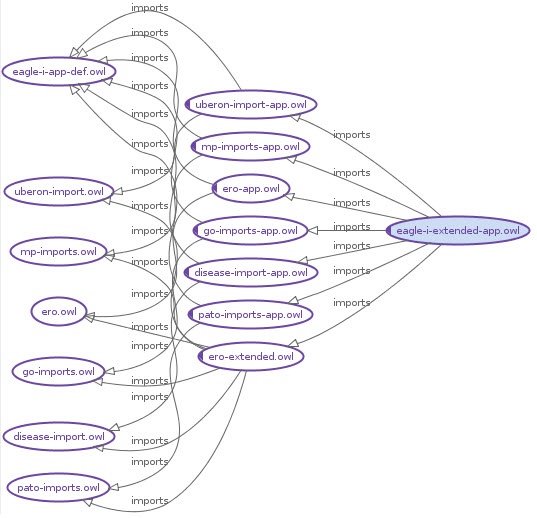
It is Finally, it is also important to have a basic understanding of the file import structure through with the complete eagle-i ontology is assembled , in order to correctly place axioms driving application functionality. Figure 1 below illustrates the import chain, and the The Table of Annotation and Domain Layer Files above describes key features and content of each file. Note that each owl file containing domain content is paired with an application file (-app.owl) that holds application axioms on domain classes/properties.
Figure 1
...
| icon | false |
|---|
See the Ontology File Structure page for more details and a diagram of the import chain.